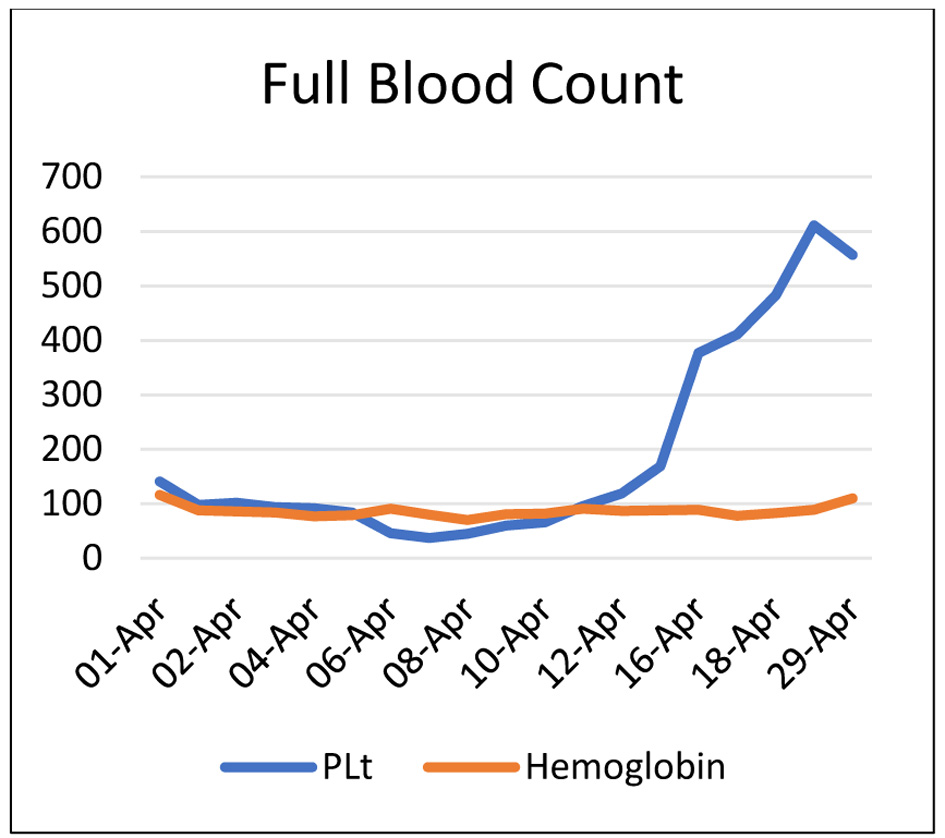
Figure 1. Full blood count.
| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jcgo.elmerpub.com |
Case Report
Volume 14, Number 3, October 2025, pages 100-105
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy or Atypical Presentation of Homolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, Low Platelets Syndrome: The Dilemma Continues
Figures

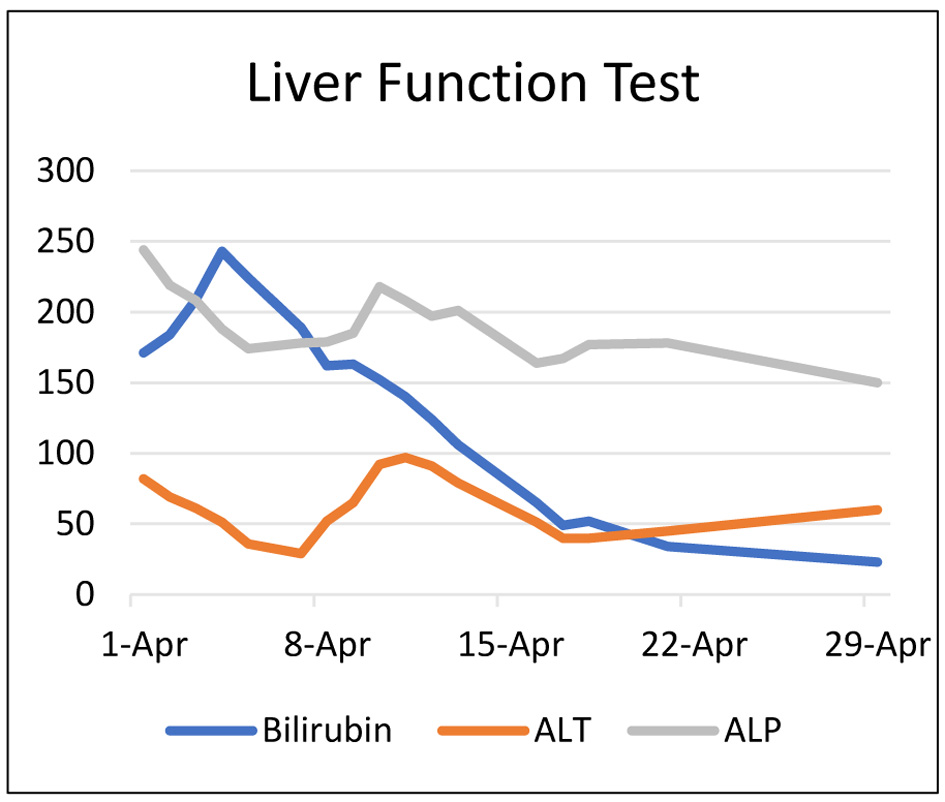
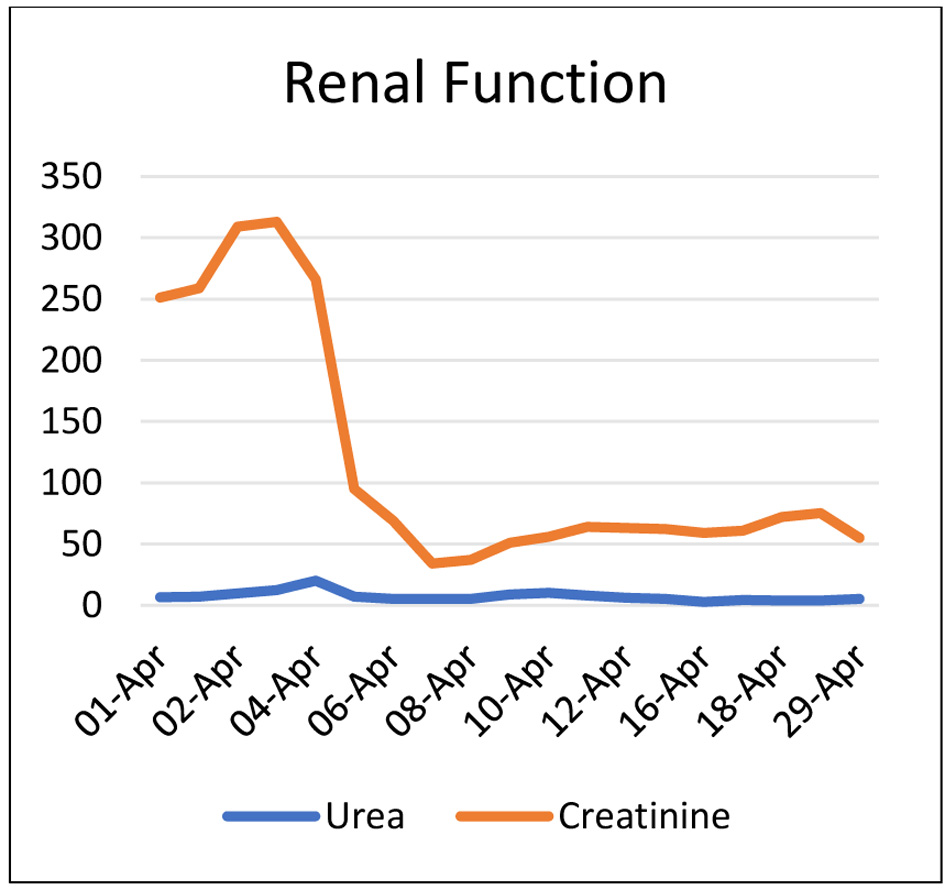
Tables
| FBC | LFT | U&E | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP: alkaline phosphatase; ALT: alanine transaminase; CRP: C-reactive protein; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; FBC: full blood count; LFT: liver function test; PLT: platelet; U&E: urea and electrolytes; WBC: white blood cell. | |||||
| Hb | 116 g/L | Bilirubin | 190 µmol/L | Na | 130 mmol/L |
| WBC | 14.9 × 109/L | ALT | 144 IU/L | K | Hemolyzed |
| PLT | 141 × 109/L | ALP | 370 IU/L | Urea | 6.7 mmol/L |
| CRP | 31.4 mg/L | Albumin | 21 g/L | Cr | 251 µmol/L |
| Amylase | 40 IU/L | eGFR | 19 mL/min | ||
| Result | Reference range | |
|---|---|---|
| aPTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; INR: international normalized ratio. | ||
| Prothrombin time | 22.1 | 9.7 - 14.1 |
| INR | 1.8 | 0.9 - 1.1 |
| aPTT | 44 | 25.1 - 36.5 |
| Fibrinogen | 1.5 | 2.7 - 5.6 |
| Result | Reference range | |
|---|---|---|
| Low serum haptoglobin, raised LDH, and conjugated bilirubin indicate hepatocellular damage. LDH: lactate dehydrogenase. | ||
| Serum haptoglobin | 0.18 g/L | 0.35 - 2.50 |
| Serum LDH | 404 U/L | 125 - 220 |
| Serum bilirubin | 163 µmol | < 21 |
| Serum conjugated bilirubin | 119.5 µmol/L | < 8.6 |
| Blood morphology | Anisocytosis | |
| HELLP: Homolysis, Elevated liver enzymes, low platelets. |
| Hemolysis, established by at least two of the following: |
| Peripheral smear with schistocytes and burr cells |
| Serum bilirubin ≥ 1.2 mg/dL (20.52 µmol/L) |
| Low serum haptoglobin (≤ 25 mg/dL) or LDH ≥ 2 times the upper level of normal |
| Severe anemia, unrelated to blood loss |
| Elevated liver enzymes: |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ≥ 2 times the upper level of normal |
| Low platelets: < 100,000 cells/µL |
| HELLP: Homolysis, Elevated liver enzymes, low platelets. |
| Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP) |
| Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) |
| Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) |
| Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) |
| Cholecystitis |
| Fulminant viral hepatitis |
| Acute pancreatitis |
| Disseminated herpes simplex |
| Hemorrhagic or septic shock |
| AFLP: acute fatty liver of pregnancy. |
| Signs and symptoms |
| Vomiting |
| Abdominal pain |
| Polydipsia/polyuria |
| Encephalopathy |
| Laboratory findings |
| Elevated bilirubin (> 0.8 mg/dL or > 14 µmol/L) |
| Hypoglycemia (glucose < 72 mg/dL or < 4 mmol/L) |
| Leukocytosis (> 11,000 cells/µL) |
| Elevated transaminases (AST or ALT) (> 42 international unit/L) |
| Elevated ammonia (> 47 µmol/L) |
| Elevated urate (5.7 mg/dL or > 340 µmol/L) |
| Acute kidney injury, or creatinine > 1.7 mg/dL (150 µmol/L) |
| Coagulopathy or prothrombin time > 14 s |
| Imaging: Ascites or bright liver on ultrasound scan |
| Histology: Microvesicular steatosis on liver biopsy |